Baidu search engine
Baidu is China’s leading search engine – you can think of it as China’s Google. And while Google has a global presence and can be accessed by Chinese users (to a degree), Baidu is the go-to search engine of choice there.
- Interested in Baidu? Check out the website here
For U.S. users and English speakers, know this: While Baidu will load in Mandarin at first, you can easily change its settings to navigate it in English.
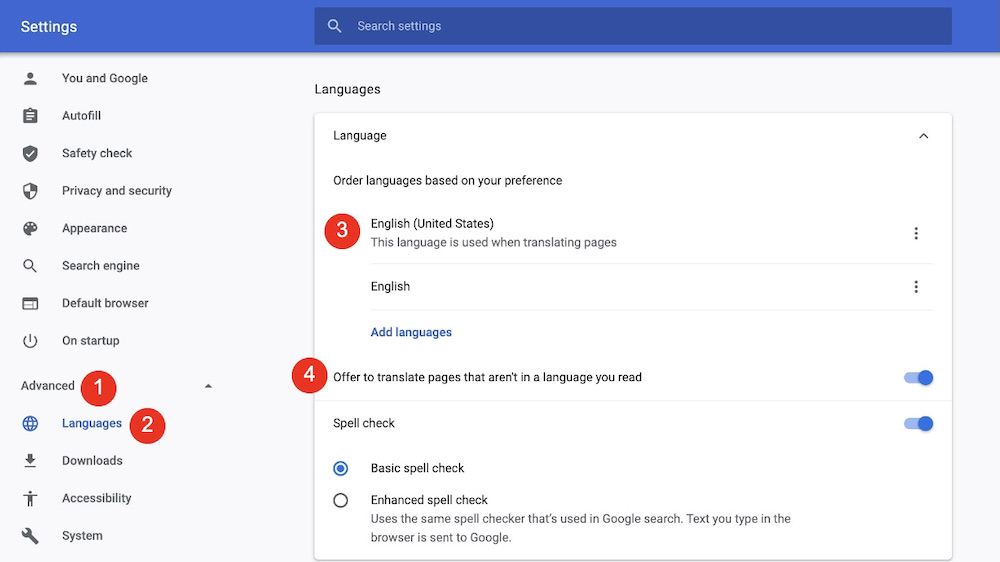
To make that change, it’s best to use Google Chrome. Click the Three-Dot icon on the top right of the page, then choose Settings. Go to Advanced > Languages, and set the This Language is Used When Translating Pages option to English (or whatever language you prefer). Next, make sure the toggle next to Offer to Translate Pages That Aren’t in a Language You Read is on. (The languages you’ve told Chrome you read are listed in that section, right above Add Languages.)
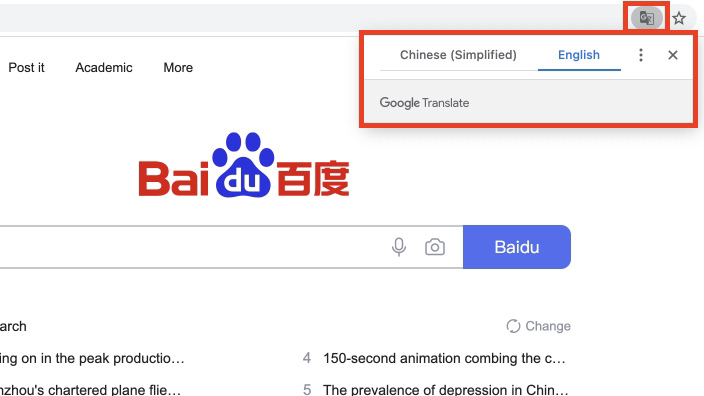
When you go to Baidu – or any site that isn’t in a language you read – you should get a pop-up to translate it. If you don’t, or if you accidentally dismiss it, click the Pages icon in the address bar. Clicking that will let you choose your language, which will translate the page.
- Also check out our roundup of the best browser
Features
Baidu can be compared to Google in terms of its products, which extend past just search. Baidu has services like maps, multimedia, and a Wikipedia-like website, among many others.
For advertisers, like brands that want to promote products or services to a Chinese audience, there’s an ad platform similar to Google’s. You can bid on keywords, which will trigger display ads. There’s also the option to pay for higher placement in search results.
Privacy
Baidu’s privacy policy is brief and easy to understand. The search engine does collect and use your personal information, particularly to customize your search experience, but does not disclose that info to third parties. Baidu uses tracking cookies, too. The website says you can reject tracking cookies, which you should be able to do in your browser.
It looks like you need a login to get into the search engine’s privacy settings to make any changes, and the login page doesn’t seem to translate. Basically, you should be comfortable with the out-of-the-box privacy settings offered by Baidu and whatever you can do with your browser – that’s likely the most assurance you’ll get.
User experience
Baidu’s translation into English isn’t perfect, and reading the results can feel a little clunky – but odds are you’re not using Baidu as your primary search engine, and getting insight into China’s top results is the real draw.
Also, using Baidu and getting the most accurate search results takes some effort. Baidu is designed to work with Chinese, not English, so searching in English won’t give you complete results. Instead, you have to search in Chinese.

For example, searching for “Disneyland” in English returns almost 16 million results.

But searching for “Disneyland” in Chinese (more on how to do that in a second) returns 100 million results, and they’re more targeted to Shanghai Disney.
This is important because if you’re marketing to a Chinese audience, you need to know what they see when they search for a specific term in Chinese, not in English. To do this, you can keep the page translation set to English, but instead of typing your search term in English, go to Google Translate. Select English in the first box and Chinese (Simplified) from the drop-down in the second box. Translate your search text, then copy and paste the Chinese characters into the Baidu search field.
Platforms
Baidu can be accessed via Baidu.com, and it’s best to use the search engine on Chrome for the translation tools.
Don’t be fooled by the “Baidu in English” website that will likely come up as a top result if you search for “Baidu.” While this search engine claims to return the same results as Baidu.com when you search in English, it also states that it’s not affiliated with Baidu in any way.
The competition
While Google is its biggest competitor globally, Baidu is the leading search engine in China (Google is highly blocked for Chinese users). Moreover, Baidu is focused on the country’s market, while Google has a global reach. Also, Baidu does a better job than Google at understanding Chinese-language searches – it has a more complex search algorithm to match the complex native language.
Final verdict
The regular internet user may not have any need for Baidu, but for brands or creators that want to reach a Chinese market, it’s an unparalleled tool.
Searching with Baidu and getting the best results possible takes some effort when it comes to translating text to and from Chinese. You have to set the home page and results pages to your language of choice (which won’t always auto-populate, so you have to click to translate), but you should search in Chinese, which requires translating your search text from English.
If you don’t mind the somewhat long-winded approach, though, and you’re either highly interested in Chinese culture, or you’re trying to reach a Chinese audience, Baidu is the preeminent search engine to use. It also has a lot of products to experiment with, and while you may not need them on a daily basis, they can be helpful to further learn what a Chinese audience is interested in.
- We've also featured the best people search finder services and engines
0 comments:
Post a Comment